Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
A new diagnostic technique that has the potential to identify opioid-addicted patients at risk for relapse could lead to better treatment and outcomes. Using an algorithm that looks for patterns in brain structure and functional connectivity, researchers were able to distinguish prescription opioid users from healthy participants. If treatment is successful, their brains will resemble the brain of someone not addicted to opioids. “People can say one thing, but brain patterns do not lie,” says lead researcher Suchismita Ray, an associate professor in the health informatics department at Rutgers School of Health Professions. “The brain patterns that the algorithm identified from brain volume and functional connectivity biomarkers from prescription opioid users hold great promise to improve over current diagnosis.” In the study in NeuroImage: Clinical, Ray and her colleagues used MRIs to look at the brain structure and function in people diagnosed with prescription opioid use disorder who were seeking treatment compared to individuals with no history of using opioids. The scans looked at the brain network believed to be responsible for drug cravings and compulsive drug use. At the completion of treatment, if this brain network remains unchanged, the patient needs more treatment. read the study at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102663 read the article at https://www.futurity.org/opioid-addiction-relapse-algorithm-2586182-2/
Via nrip
Researchers at Duke University are developing an artificial intelligence tool for toilets that would help providers improve care management for patients with gastrointestinal issues through remote patient monitoring. The tool, which can be installed in the pipes of a toilet and analyzes stool samples, has the potential to improve treatment of chronic gastrointestinal issues like inflammatory bowel disease or irritable bowel syndrome, according to a press release. When a patient flushes the toilet, the mHealth platform photographs the stool as it moves through the pipes. That data is sent to a gastroenterologist, who can analyze the data for evidence of chronic issues. A study conducted by Duke University researchers found that the platform had an 85.1 percent accuracy rate on stool form classification and a 76.3 percent accuracy rate on detection of gross blood. read the entire article at https://mhealthintelligence.com/news/ai-toilet-tool-offers-remote-patient-monitoring-for-gastrointestinal-health
Via nrip
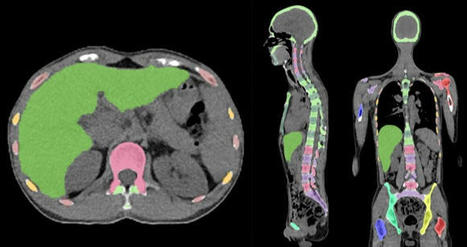
Skeleton/bone marrow involvement in patients with newly diagnosed Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) is an important predictor of adverse outcomes1. Studies show that FDG-PET/CT upstages patients with uni- or multifocal skeleton/bone marrow uptake (BMU) when iliac crest bone marrow biopsy fails to find evidence of histology-proven involvement. The general recommendation is, therefore, that bone marrow biopsy can be avoided when FDG-PET/CT is performed at staging. Our aim was to develop an AI-based method for the detection of focal skeleton/BMU and quantification of diffuse BMU in patients with HL undergoing staging with FDG-PET/CT. The output of the AI-based method in a separate test set was compared to the image interpretation of ten physicians from different hospitals. Finally, the AI-based quantification of diffuse BMU was compared to manual quantification. Artificial intelligence-based classification A convolutional neural network (CNN) was used to segment the skeletal anatomy11. Based on this CNN, the bone marrow was defined by excluding the edges from each individual bone; more precisely, 7 mm was excluded from the humeri and femora, 5 mm was excluded from the vertebrae and hip bones, and 3 mm was excluded from the remaining bones. Focal skeleton/bone marrow uptake The basic idea behind our approach is that the distribution of non-focal BMU has a light tail and most pixels will have an uptake reasonably close to the average. There will still be variations between different bones. Most importantly, we found that certain bones were much more likely to have diffuse BMU than others. Hence, we cannot use the same threshold for focal uptake in all bones. At the other end, treating each bone individually is too susceptible to noise. As a compromise, we chose to divide the bones into two groups: -
“spine”—defined as the vertebrae, sacrum, and coccyx as well as regions in the hip bones within 50 mm from these locations, i.e., including the sacroiliac joints. -
“other bones”—defined as the humeri, scapulae, clavicles, ribs, sternum, femora, and the remaining parts of the hip bones. For each group, the focal standardized uptake values (SUVs) were quantified using the following steps: - Threshold computation. A threshold (THR) was computed using the mean and standard deviation (SD) of the SUV inside the bone marrow. The threshold was set to
- 2. Abnormal bone region. The abnormal bone region was defined in the following way:
Only the pixels segmented as bone and where SUV > THR were considered. To reduce the issues of PET/CT misalignment and spill over, a watershed transform was used to assign each of these pixels to a local maximum in the PET image. If this maximum was outside the bone mask, the uptake was assumed to be leaking into the bone from other tissues and was removed. Finally, uptake regions smaller than 0.1 mL were removed. - 3.Abnormal bone SUV quantification. The mean squared abnormal uptake (MSAU) was first calculated as
MSAU=meanof(SUV−THR)2overtheabnormalboneregion. To quantify the abnormal uptake, we used the total squared abnormal uptake (TSAU), rather than the more common total lesion glycolysis (TLG). We believe TLG tends to overestimate the severity of larger regions with moderate uptake. TSAU will assign a much smaller value to such lesions, reflecting the uncertainty that is often associated with their classification. Instead, TSAU will give a larger weight to small lesions with very high uptake. This reflects both the higher certainty with respect to their classification and the severity typically associated to very high uptake. TSAU=MSAU×(volumeoftheabnormalboneregion). This calculation leads to two TSAU values; one for the “spine” and one for the “other bones”. As the TSAU value can be nonzero even for patients without focal uptake, cut-off values were tuned using the training cohort. The AI method was adjusted in the training group to have a positive predictive value of 65% and a negative predictive value of 98%. For the “spine”, a cut-off of 0.5 was used, and for the “other bones”, a cut-off of 3.0 was used. If one of the TSAU values was higher than the corresponding cut-off, the patient was considered to have focal uptake. Results Focal uptake Fourteen of the 48 cases were classified as having focal skeleton/BMU by the AI-based method. The majority of physicians classified 7/48 cases as positive and 41/48 cases as negative for having focal skeleton/BMU. The majority of the physicians agreed with the AI method in 39 of the 48 cases. Six of the seven positive cases (86%) identified by the majority of physicians were identified as positive by the AI method, while the seventh was classified as negative by the AI method and by three of the ten physicians. Thirty-three of the 41 negative cases (80%) identified by the majority of physicians were also classified as negative by the AI method. In seven of the remaining eight patients, 1–3 physicians (out of the ten total) classified the cases as having focal uptake, while in one of the eight cases none of the physicians classified it as having focal uptake. These findings indicate that the AI method has been developed towards high sensitivity, which is necessary to highlight suspicious uptake. Conclusions The present study demonstrates that an AI-based method can be developed to highlight suspicious focal skeleton/BMU in HL patients staged with FDG-PET/CT. This AI-based method can also objectively provide results regarding high versus low BMU by calculating the SUVmedian value in the whole spine marrow and the liver. Additionally, the study also demonstrated that inter-observer agreement regarding both focal and diffuse BMU is moderate among nuclear medicine physicians with varying levels of experience working at different hospitals. Finally, our results show that the automated method regarding diffuse BMU is comparable to the manual ROI method. read the original paper at https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-89656-9
Via nrip
New artificial intelligence technology that uses a common CT angiography (CTA), as opposed to the more advanced imaging normally required to help identify patients who could benefit from endovascular stroke therapy (EST), is being developed at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth). Two UTHealth researchers worked together to create a machine-learning artificial intelligence tool that could be used for assessing a stroke at every hospital that takes care of stroke patients - not just at large academic hospitals in major cities. Research to further develop and test the technology tool is funded through a five-year, $2.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). "The vast majority of stroke patients don't show up at large hospitals, but in those smaller regional facilities. And most of the emphasis on screening techniques is only focused on the technologies used in those large academic centers. With this technology, we are looking to change that," said Sunil Sheth, MD, assistant professor of neurology at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth. Sheth set out with Luca Giancardo, PhD, assistant professor with the Center for Precision Health at UTHealth School of Biomedical Informatics, to develop a quicker way to assess patients. The result was a novel deep neural network architecture that leverages brain symmetry. Using CTAs, which are more widely available, the system can determine the presence or absence of a large vessel occlusion and whether the amount of "at-risk" tissue is above or below the thresholds seen in those patients who benefitted from EST in the clinical trials. "This is the first time a data set is being specifically collected aiming to address the lack of quality imaging available for stroke patients at smaller hospitals," Giancardo said. read the complete press release with further details on the work at https://www.uth.edu/news/story.htm?id=9fccdefb-ff91-4775-a759-a786689956ea
Via nrip
People often turn to technology to manage their health and wellbeing, whether it is - to record their daily exercise,
- measure their heart rate, or increasingly,
- to understand their sleep patterns.
Sleep is foundational to a person’s everyday wellbeing and can be impacted by (and in turn, have an impact on) other aspects of one’s life — mood, energy, diet, productivity, and more. As part of Google's ongoing efforts to support people’s health and happiness, Google has announced Sleep Sensing in the new Nest Hub, which uses radar-based sleep tracking in addition to an algorithm for cough and snore detection. The new Nest Hub, with its underlying Sleep Sensing features, is the first step in empowering users to understand their nighttime wellness using privacy-preserving radar and audio signals. Understanding Sleep Quality with Audio Sensing The Soli-based sleep tracking algorithm gives users a convenient and reliable way to see how much sleep they are getting and when sleep disruptions occur. However, to understand and improve their sleep, users also need to understand why their sleep is disrupted. To assist with this, Nest Hub uses its array of sensors to track common sleep disturbances, such as light level changes or uncomfortable room temperature. In addition to these, respiratory events like coughing and snoring are also frequent sources of disturbance, but people are often unaware of these events. As with other audio-processing applications like speech or music recognition, coughing and snoring exhibit distinctive temporal patterns in the audio frequency spectrum, and with sufficient data an ML model can be trained to reliably recognize these patterns while simultaneously ignoring a wide variety of background noises, from a humming fan to passing cars. The model uses entirely on-device audio processing with privacy-preserving analysis, with no raw audio data sent to Google’s servers. A user can then opt to save the outputs of the processing (sound occurrences, such as the number of coughs and snore minutes) in Google Fit, in order to view personal insights and summaries of their night time wellness over time. read the entire unedited blog post at https://ai.googleblog.com/2021/03/contactless-sleep-sensing-in-nest-hub.html
Via nrip
|
Researchers investigating the benefits of 3D printing technology found it can deliver significant improvements to the running of hospitals. The research, which compared the drawbacks and advantages of using 3D printing technology in hospitals, has been published in the International Journal of Operations and Production Management. The study revealed that introducing such technology into hospitals could help alleviate many of the strains the UK healthcare system and healthcare systems worldwide face. Boosting surgery success rates - 3D printing makes it possible for surgical teams to print 3D models based on an individual patient’s surgical needs, providing more detailed and exact information for the surgeon to plan and practice the surgery, minimising the risk of error or unexpected complications. - the use of 3D printed anatomical models was useful when communicating the details of the surgery with the patient, helping to increase their confidence in the procedure. Speeding up patient recovery time - significant reduction in post-surgery complications, patient recovery times and the need for subsequent hospital appointments or treatments. Speeding up procedures - provide surgeons with custom-built tools for each procedure, with the findings revealing that surgeries with durations of four to eight hours were reduced by 1.5 to 2.5 hours when patient-specific instruments were used. - could also make surgeries less invasive (for example, removing less bone or tissue) - result in less associated risks for the patient (for example, by requiring less anaesthesia). Real-life training opportunities - enables trainee surgeons to familiarise themselves with the steps to take in complex surgeries by practicing their skills on examples that accurately replicate real patient problems, and with greater variety. Careful consideration required Despite the research showing strong and clear benefits of using 3D printing, Dr Chaudhuri and his fellow researchers urge careful consideration for the financial costs. 3D printing is a significant financial investment for hospitals to make. In order to determine whether such an investment is worthwhile, the researchers have also developed a framework to aid hospital decision-makers in determining the return on investment for their particular institution. read the study at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344956611_Accepted_for_publication_in_International_Journal_of_Operations_and_Production_Management_Should_hospitals_invest_in_customised_on-demand_3D_printing_for_surgeries read more at https://www.healtheuropa.eu/3d-printing-technology-boosts-hospital-efficiency-and-eases-pressures/108544/
Lire l'article complet sur : www.healtheuropa.eu
Via nrip
The Future of Health care needs Doctors and Technologists to work well together
In a new report - The Truth About Doctors - Covid 19 Edition, McCann Health identifies four key ways how health care technology has changed since 2016. It highlights the the role of the health care industry in leveraging these changes to carve a new way forward In the past, technology has been gradually revolutionizing health care. While patients have adopted it whole heartedly, It has received push back from various quarters of care providers. Many think it may be having less-positive effects for physicians, some of whom eye it as a threat to doctoring. However, come Covid-19, and the world simultaneously looked up to technology and the medical community in more or less an equal measure. They wanted Tech to help us navigate the pandemic and the medical community to get us out of it, and the need for both to work together and amplify became clearer with each day since the pandemic started As the world moves towards a period of renewal, it will be increasingly important that technology plays a complementary role in care, not just supporting doctoring but super-powering it. Lets look at the 4 main focus areas mentioned in the report. Technology is redefining the where of care Home defines most individuals’ physical, mental, and social health. Until recently, home has also been a place where doctors are absent. That changed with Covid-19 and the rapid growth of telemedicine If marketers and others within the health care industry can help doctors acclimatize to the new where of care — supporting them to embrace the home as an extension of their domain rather than something outside of it — health can be elevated in a more holistic level. Technology can help cultivate inter-professional collaboration During the pandemic, by using social media and messaging platforms like Twitter and WhatsApp, doctors with diverse backgrounds were able to pool knowledge and emotionally support each other in the collective effort to fight Covid-19. They collaborated in new ways with allied health care professionals, government, and industry, sparking a reimagining of the health ecosystem. The challenge moving forward is giving this organic way of working across care teams and borders a structure to make it scalable. How can the health care system evolve so an expert in peripheral neuropathy in Australia can collaborate with a startup in Belgium? On a more local level, how can health care systems ensure that the different health professionals involved in a patient’s care work together? Secure, shared platforms can nurture a sense of belonging and create a new kind of community for doctors — a “care tribe” that has the power to connect perspectives and passions to advance the experience of care. Technology can foster continuity and ‘contiguity’ There is a new willingness to take control over personal well-being in light of the pandemic. However this can only go so far in a health care system where time is limited and resources are fragmented. With the proliferation of sensors there may be no better time to apply the quantifiable self to achieve more personalized care. However, new self-monitoring technologies must be integrated with the full health care ecosystem to make personal health care easier and more seamless, rather than adding to the confusion. Even if technology provides access to more health information, it does not necessarily follow that patients or health care providers will understand it. Health care providers must be taught the skills to not only help patients decipher their health information but to advance their care by proactively identifying and addressing their health risks. With this comes a need to ensure that work is being done in a way that overcomes health inequities rather than heightens them. Technology can care for the carers Covid-19 has shown that, instead of posing an existential threat to doctors, technology may be a lifeline for them. By assessing patients before a consult, tech platforms can allow doctors to channel their energy to the problems that need it most. In complicated therapy areas such as oncology, it can ease their load through supporting diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. In the day-to-day practice of caregiving, technology can enrich relationships by enabling doctors to focus on the human art of medicine. Combined with the flexibility of video consultations and the panoramic perspective of integrated systems, technology can give doctors their time back to practice care on their own terms. It’s easy to think that health care is behind the curve when it comes to embracing technology. Covid-19 has shown that this just isn’t the case. When it comes to the relationship between doctors and technology, the pandemic has been an epiphany. Instead of displacing doctors, technology has the power to help them provide better care, supercharging the humanity and empathy that lies at the heart of medicine. Technology has a role in medicine, especially in the service of care. along with my own insights and thoughts
Via nrip
As the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in health applications grows, health providers are looking for ways to improve patients' experience with their machine doctors. Researchers from Penn State and University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB) found that people may be less likely to take health advice from an AI doctor when the robot knows their name and medical history. On the other hand, patients want to be on a first-name basis with their human doctors. When the AI doctor used the first name of the patients and referred to their medical history in the conversation, study participants were more likely to consider an AI health chatbot intrusive and also less likely to heed the AI's medical advice, the researchers added. However, they expected human doctors to differentiate them from other patients and were less likely to comply when a human doctor failed to remember their information. The findings offer further evidence that machines walk a fine line in serving as doctors. Machines do have advantages as medical providers, said Joseph B. Walther, distinguished professor in communication and the Mark and Susan Bertelsen Presidential Chair in Technology and Society at UCSB. He said that, like a family doctor who has treated a patient for a long time, computer systems could — hypothetically — know a patient’s complete medical history. In comparison, seeing a new doctor or a specialist who knows only your latest lab tests might be a more common experience, said Walther, who is also director of the Center for Information Technology and Society at UCSB. “This struck us with the question: ‘Who really knows us better: a machine that can store all this information, or a human who has never met us before or hasn’t developed a relationship with us, and what do we value in a relationship with a medical expert?’” said Walther. “So this research asks, who knows us better — and who do we like more?” Accepting AI doctors As medical providers look for cost-effective ways to provide better care, AI medical services may provide one alternative. However, AI doctors must provide care and advice that patients are willing to accept, according to Cheng Chen, doctoral student in mass communications at Penn State. “One of the reasons we conducted this study was that we read in the literature a lot of accounts of how people are reluctant to accept AI as a doctor,” said Chen. “They just don’t feel comfortable with the technology and they don’t feel that the AI recognizes their uniqueness as a patient. So, we thought that because machines can retain so much information about a person, they can provide individuation, and solve this uniqueness problem.” The findings suggest that this strategy can backfire. “When an AI system recognizes a person’s uniqueness, it comes across as intrusive, echoing larger concerns with AI in society,” said Sundar. In the future, the researchers expect more investigations into the roles that authenticity and the ability for machines to engage in back-and-forth questions may play in developing better rapport with patients. read more at https://news.psu.edu/story/657391/2021/05/10/research/patients-may-not-take-advice-ai-doctors-who-know-their-names
Lire l'article complet sur : news.psu.edu
Via nrip
Two scientific leaps, in machine learning algorithms and powerful biological imaging and sequencing tools , are increasingly being combined to spur progress in understanding diseases and advance AI itself. Cutting-edge, machine-learning techniques are increasingly being adapted and applied to biological data, including for COVID-19. Recently, researchers reported using a new technique to figure out how genes are expressed in individual cells and how those cells interact in people who had died with Alzheimer's disease. Machine-learning algorithms can also be used to compare the expression of genes in cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 to cells treated with thousands of different drugs in order to try to computationally predict drugs that might inhibit the virus. While, Algorithmic results alone don't prove the drugs are potent enough to be clinically effective. But they can help identify future targets for antivirals or they could reveal a protein researchers didn't know was important for SARS-CoV-2, providing new insight on the biology of the virus read the original article which speaks about a lot more at https://www.axios.com/ai-machine-learning-biology-drug-development-b51d18f1-7487-400e-8e33-e6b72bd5cfad.html
Via nrip
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...