 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Comment fonctionne ChatGPT ?
Technologie : Cet article vous plonge dans les rouages de ChatGPT, le chatbot d'IA extrêmement populaire. Alors, si vous voulez savoir comment s'opère la magie de l'IA générative, lisez la suite.
Via Gust MEES
New artificial intelligence technology that uses a common CT angiography (CTA), as opposed to the more advanced imaging normally required to help identify patients who could benefit from endovascular stroke therapy (EST), is being developed at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth). Two UTHealth researchers worked together to create a machine-learning artificial intelligence tool that could be used for assessing a stroke at every hospital that takes care of stroke patients - not just at large academic hospitals in major cities. Research to further develop and test the technology tool is funded through a five-year, $2.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). "The vast majority of stroke patients don't show up at large hospitals, but in those smaller regional facilities. And most of the emphasis on screening techniques is only focused on the technologies used in those large academic centers. With this technology, we are looking to change that," said Sunil Sheth, MD, assistant professor of neurology at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth. Sheth set out with Luca Giancardo, PhD, assistant professor with the Center for Precision Health at UTHealth School of Biomedical Informatics, to develop a quicker way to assess patients. The result was a novel deep neural network architecture that leverages brain symmetry. Using CTAs, which are more widely available, the system can determine the presence or absence of a large vessel occlusion and whether the amount of "at-risk" tissue is above or below the thresholds seen in those patients who benefitted from EST in the clinical trials. "This is the first time a data set is being specifically collected aiming to address the lack of quality imaging available for stroke patients at smaller hospitals," Giancardo said. read the complete press release with further details on the work at https://www.uth.edu/news/story.htm?id=9fccdefb-ff91-4775-a759-a786689956ea
Via nrip
Imagine you’re a scientist who needs to discover a new antibiotic to fight off a scary disease. How would you go about finding it? Typically, you’d have to test lots and lots of different molecules in the lab until you find one that has the necessary bacteria-killing properties. You might find some contenders that are good at killing the bacteria only to realize that you can’t use them because they also prove toxic to humans. It’s a very long, very expensive, and probably very aggravating process. But what if, instead, you could just type into your computer the properties you’re looking for and have your computer design the perfect molecule for you? That’s the general approach IBM researchers are taking, using an AI system that can automatically generate the design of molecules for new antibiotics. In a new paper, published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, the researchers detail how they’ve already used it to quickly design two new antimicrobial peptides — small molecules that can kill bacteria — that are effective against a bunch of different pathogens in mice. Normally, this molecule discovery process would take scientists years. The AI system did it in a matter of days. That’s great news, because we urgently need faster ways to create new antibiotics. How IBM’s AI system works IBM’s new AI system relies on something called a generative model. To understand it at its simplest level, we can break it down into three basic steps. First, the researchers start with a massive database of known peptide molecules. Then the AI pulls information from the database and analyzes the patterns to figure out the relationship between molecules and their properties. It might find that when a molecule has a certain structure or composition, it tends to perform a certain function. This allows it to “learn” the basic rules of molecule design. Finally, researchers can tell the AI exactly what properties they want a new molecule to have. They can also input constraints (for example: low toxicity, please!). Using this info on desirable and undesirable traits, the AI then designs new molecules that satisfy the parameters. The researchers can pick the best one from among them and start testing on mice in a lab. The IBM researchers claim that their approach outperformed other leading methods for designing new antimicrobial peptides by 10 percent. They found that they were able to design two new antimicrobial peptides that are highly potent against diverse pathogens, including multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae, a bacterium known for causing infections in hospital patients. Happily, the peptides had low toxicity when tested in mice, an important signal about their safety (though not everything that’s true for mice ends up being generalizable to humans). read the original unedited article at https://www.vox.com/future-perfect/22360573/ai-ibm-design-new-antibiotics-covid-19-treatments read the paper by the IBM researchers - Accelerated antimicrobial discovery via deep generative models and molecular dynamics simulations
Via nrip
A deep learning tool was able to classify subtypes of lung cancer with the same level of accuracy as human pathologists, according to a study conducted by Dartmouth’s Norris Cotton Cancer Center and published in Scientific Reports.
Via Dominique Godefroy, Philippe Marchal
The human body is frail and people end up in intensive care units for all kinds of reasons. Whatever brings them there, more than half of adults admitted to an ICU end up sharing the same potentially life-threatening condition: kidney damage known as acute kidney injury.
The Veterans Administration thinks artificial intelligence could reduce the toll. In a project that drew on roughly 700,000 medical records from US veterans, the agency worked with Google parent Alphabet’s DeepMind unit to create software that attempts to predict which patients are likely to develop AKI. The VA hopes to test whether those predictions can help doctors prevent people from developing the condition. AKI manifests as a sudden failure of the kidneys to properly remove waste from the body, and often occurs as a complication of surgery, infection, or other stresses of hospitalization.
The project is an example of the worldwide push to save lives using the AI techniques that power internet companies’ virtual assistants and facial recognition. The spread of digital health records offers a torrent of data about patients, including subtle patterns that algorithms can interpret in ways doctors cannot. In the US and other rich countries, AI is seen as a way to improve care and cut costs. In places like India and China with chronic shortages of medical specialists, the technology could improve access to care.
DeepMind’s collaboration with the VA fits into a broader push into health care by Alphabet. The company hopes to use AI to diversify beyond advertising, which supplies nearly 90 percent of its revenue. Other Alphabet projects are training algorithms to detect eye disease and cancer. Google recently hired veteran health system executive David Feinberg to take charge of its health projects.
Via Dominique Godefroy
300 million people are affected by asthma globally, and 100 million are suffering from the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The treatment of these two diseases costs over €80 billion in the US and Europe each. The direct costs make up almost $50.1 billion, and hospital stays are the most significant part of that cost. For adults, asthma is one of the top reason for underperformance at work. Sufferers miss about 14 million workdays each year, and this equals about $2 billion of indirect asthma costs.
Patients first realize that they have a chronic pulmonary disease like asthma or COPD if symptoms like recurrent wheezing, coughing or difficulty in breathing appear. A pulmonologist would then use a spirometer to formally diagnose the condition. The pulmonologist then managed by a combination of lifestyle choices and medication. Lifestyle choices include avoiding triggers such as cigarette smoke, pets, or aspirin. Medication is generally inhaled using an inhaler and can be quick-relief medications (such as beta2-adrenoceptor agonists or salbutamol) or long-term control medication (such as corticosteroids or Long-acting beta-adrenoceptor agonists).
Given that controlling lifestyle choices are a big part of preventing and managing chronic pulmonary diseases, smart medical devices such as smart inhalers and smart spirometers could have a significant impact on health outcomes. Here are 5 different ways in which AI is redefining respiratory care
Via Dominique Godefroy
Medtronic has announced that it will acquire long-time partner Nutrino, an AI powered personalized nutrition platform for an undisclosed sum.
As part of the deal Medtronic will be integrating Nutrino’s AI-driven personalized insights and food database. The acquisition is set to specifically boost Medtronic’s offerings for people living with diabetes and offer the company’s predictive glycemic response algorithm, which will be integrated with Medtronic’s CGM system.
"Bringing Nutrino and their nutrition-related expertise into our organization will give us a substantial differentiator in the diabetes industry and accelerate our progress to help people with diabetes live with greater freedom and better health," Hooman Hakami, executive vice president and president of the Diabetes Group at Medtronic, said in a statement. "The Nutrino team has been an outstanding partner over the past few years. We are excited to welcome them to our team, and I have no doubt that, together, we will make a profound impact on the lives of people with diabetes.”
Via Dominique Godefroy
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly permeating medical imaging, but its integration into clinical practice will depend on the capacity of AI technology to facilitate workflow.
Virtual reality goggles and medical images.
Wiro J Niessen is Professor of biomedical image analysis at Erasmus MC in Rotterdam and Delft University of Technology, and Director of the biomedical image analysis platform of the European Organization for Imaging Research. For the past 20 years, he has been working to integrate AI in radiology. He believes the technology can help radiologists in countless scenarios from automating image analysis to picking up disease at pre-clinical stage and predicting treatment outcome. But a number of obstacles must be overcome before it fully enters clinical practice.
Myriad applications for AI in radiology
One of Niessen’s key responsibilities has been to apply AI to support the Rotterdam study, a population cohort that was launched 15 years ago at Erasmus MC, and in which thousands of images have been generated to collect information on disease development. Niessen has been using machine learning (ML) for the past 15 years, first to automate the analysis of large imaging data sets, and now to find patterns with a prognostic value.
“We started to make the clinical researchers’ and clinicians’ jobs easier by automating the extraction of quantitative information from imaging data, which is tedious and time consuming to do by hand.
“Now we also try to predict from a CT or MRI scan whether someone is going to respond to a certain therapy or if they are likely to at an early stage in neurodegenerative disease. If you collect a lot of data and follow the patients over time, you see whether they develop a disease or not, and whether they respond to therapy. You can always dive back into the data and see whether there are patterns that can predict disease,” he said.
Niessen, who talked to Insights at the European Congress of Radiology in Vienna, is involved at every stage of AI technology development, from research all the way up to commercialisation. He notably founded the Erasmus MC spin-off company Quantib, which brings solutions that were initiated in research to the market.
For a long time, he has only used conventional ML, first selecting relevant features in an image, and then assessing their diagnostic or prognostic value. In oncology imaging, that means for instance capturing the boundaries of a tumour and computing features such as tumour texture, volume, intensity patterns and density, to build classifiers that can help in diagnosis and prognosis. Niessen’s group has worked with common ML tools such as support vector machines, decision trees and random forests.
Via Dominique Godefroy
Healthcare executives expect artificial intelligence to be among the most impactful technologies fueling innovation, but few are crafting strategies to advance emerging AI applications. That means now is the time to not only invest but also take on a proactive role in developing new tools.
That's why we are focusing on artificial intelligence in November with analysis, insights from innovators and established healthcare providers using AI and machine learning, as well as tactics and strategies for planning and putting the tech to work. Read all of our Focus on Artificial Intelligence articles here, all month long.
For our new deep dive into AI, HIMSS Media surveyed 180 qualified professionals in provider and non-provider settings about how they're putting it to work. Respondents, who work in IT management, clinical and business roles, were asked about their greatest security concerns, the most common ways they’re addressing the issues and who in their organizations are making decisions on strategy and internal policy.
The following three charts demonstrate what we found.
Via Dominique Godefroy
After 3 years as head of IBM’s health division, Deborah DiSanzo is leaving her role. A company spokesman said that DiSanzo will no longer lead IBM Watson Health, the Cambridge-based division that has pitched the company’s famed artificial intelligence capabilities as solutions for a myriad of health challenges, like treating cancer and analyzing medical images. Even as it has heavily advertised the potential of Watson Health, IBM has not met lofty expectations in some areas. Its flagship cancer software, which used artificial intelligence to recommend courses of treatment, has been ridiculed by some doctors inside and outside of the company. And it has struggled to integrate different technologies from other businesses it has acquired, laying off employees in the process. more at https://www.statnews.com/2018/10/19/head-of-ibm-watson-health-leaving-post/
Via nrip
Algorithms based on machine learning and deep learning, intended for use in diagnostic imaging, are moving into the commercial pipeline. However, providers will have to overcome multiple challenges to incorporate these tools into daily clinical workflows in radiology. There now are numerous algorithms in various stages of development and in the FDA approval process, and experts believe that there could eventually be hundreds or even thousands of AI-based apps to improve the quality and efficiency of radiology. The emerging applications based on machine learning and deep learning primarily involve algorithms to automate such processes in radiology as detecting abnormal structures in images, such as cancerous lesions and nodules. The technology can be used on a variety of modalities, such as CT scans and X-rays. The goal is to help radiologists more effectively detect and track the progression of diseases, giving them tools to enhance speed and accuracy, thus improving quality and reducing costs. While the number of organizations incorporating these products into daily workflows is small today, experts expect many providers to adopt these solutions as the industry overcomes implementation challenges. Data dump
Radiologists’ growing appreciation for AI may result from the technology’s promise to help the profession cope with an explosion in the amount of data for each patient case. Radiologists also are grappling with the growth in data from sources outside radiology, such as lab tests or electronic medical records. This is another area where AI could help radiologists by analyzing data from disparate sources and pulling out key pieces of information for each case,. There are other issues that AI could address as well, such as “observer fatigue,” which is an “aspect of radiology practice and a particular issue in screening examinations where the likelihood of finding a true positive is low,” wrote researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in a 2018 article in the Journal of the American College of Radiology. These researchers foresee the utility of an AI program that could identify cases from routine screening exams with a likely positive result and prioritize those cases for radiologists’ attention. AI software also could help radiologists improve worklists of cases in which referring physicians already suspect that a medical problem exists. read more at the original source: https://www.healthdatamanagement.com/news/algorithms-begin-to-show-practical-use-in-diagnostic-imaging
Via nrip
Information technology has allowed much of our economy to automate processes. We have seen transformations of the airline, banking, brokerage, entertainment, lodging, music, printing, publishing, shipping and taxi industries through the availability of massive volumes of real-time price and service data. Across America, consumer-facing retail service continues to shift to a virtual environment. Healthcare is the exception. Many health information technology (health IT) products initially focused on billing. The misalignment between billing support and the sense that these tools do not materially automate clinician work to build in efficiencies or improve workflows adds to an overall frustration with the increasing amount of time providers spend at their screens. Automation is hard because it tends to require interfaces of various types – both to other machines (Internet of Things) and to humans. Often automation proposals involve solutions that focus on highly structured data. But, someone or something has to put energy (physician salary, for example) into organizing much of this information, assuming it is even knowable. The underlying disease or patient behavior (e.g., smoking) is also often not knowable. And, automation relying on machine to machine interfaces regularly runs into a lack of application programming interfaces (APIs) supporting complex clinical data flows. I posted this week old piece now and now when it was published as #NHITWeek is this week. A lot of posts this week deal with possibilities and problems with healthcare focussed automation. The original unedited piece can be read at https://www.himss.org/news/healthcare-automation-transforming-medicine
Via nrip
Organizations continue to adapt their IT infrastructure to accommodate healthcare artificial intelligence (AI) as IT systems become more complex and data sets become more robust.
IDC predicts that spending on cognitive and AI technologies will triple by 2022 at CAGR of 37 percent.
“The market for AI continues to grow at a rapid pace,” said David Schubmehl, research director, Cognitive/Artificial Intelligence Systems at IDC. “Vendors looking to take advantage of AI, deep learning and machine learning need to move quickly to gain a foothold in this emergent market. IDC is already seeing that organizations using these technologies to drive innovation are benefitting in terms of revenue, profit, and overall leadership in their respective industries and segments.”
The AI market will see the most growth in the software segment covering nearly 40 percent of all AI spending, according to IDC. This area includes conversational AI applications such as chatbots and personal assistants, and deep learning and machine learning applications.
Server and storage hardware are predicted to be the rea wit the second most growth at the beginning of the forecast period but will taper off in favor of related IT business services, like remote hosting and cloud storage.
The biggest use of AI powered automation will be in automated threat intelligence and prevention and automated preventive maintenance.
“Worldwide cognitive/artificial intelligence spending has moved beyond the early adopters to mainstream industry-wide use case implementation,” said Marianne Daquila, research manager Customer Insights & Analysis at IDC. “Early adopters in banking, retail and manufacturing have successfully leveraged cognitive/AI systems as part of their digital transformation strategies.”
“These strategies have helped companies personalize their relationship with customers, thwart fraudulent losses, and keep factories running,” she continued. “Increasingly, we are seeing more local governments keeping people safe with cognitive/AI systems. There is no doubt that the predicted double-digit year-over-year growth will be driven by even more decision makers, across all industries, who do not want to be left behind.”
Via Dominique Godefroy
|
Researchers at Duke University are developing an artificial intelligence tool for toilets that would help providers improve care management for patients with gastrointestinal issues through remote patient monitoring. The tool, which can be installed in the pipes of a toilet and analyzes stool samples, has the potential to improve treatment of chronic gastrointestinal issues like inflammatory bowel disease or irritable bowel syndrome, according to a press release. When a patient flushes the toilet, the mHealth platform photographs the stool as it moves through the pipes. That data is sent to a gastroenterologist, who can analyze the data for evidence of chronic issues. A study conducted by Duke University researchers found that the platform had an 85.1 percent accuracy rate on stool form classification and a 76.3 percent accuracy rate on detection of gross blood. read the entire article at https://mhealthintelligence.com/news/ai-toilet-tool-offers-remote-patient-monitoring-for-gastrointestinal-health
Via nrip
Two scientific leaps, in machine learning algorithms and powerful biological imaging and sequencing tools , are increasingly being combined to spur progress in understanding diseases and advance AI itself. Cutting-edge, machine-learning techniques are increasingly being adapted and applied to biological data, including for COVID-19. Recently, researchers reported using a new technique to figure out how genes are expressed in individual cells and how those cells interact in people who had died with Alzheimer's disease. Machine-learning algorithms can also be used to compare the expression of genes in cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 to cells treated with thousands of different drugs in order to try to computationally predict drugs that might inhibit the virus. While, Algorithmic results alone don't prove the drugs are potent enough to be clinically effective. But they can help identify future targets for antivirals or they could reveal a protein researchers didn't know was important for SARS-CoV-2, providing new insight on the biology of the virus read the original article which speaks about a lot more at https://www.axios.com/ai-machine-learning-biology-drug-development-b51d18f1-7487-400e-8e33-e6b72bd5cfad.html
Via nrip
La Région Île-de-France lance le « AI for Health Challenge 2019 » : premier Challenge international sur l’oncologie à destination des startups, PME, ETI et laboratoires en partenariat avec l’Institut Gustave Roussy, Médicen et Cancer Campus.
Via ACCURAY FRANCE
Artificial intelligence could soon be used to predict a patient’s future risk of heart attack or stroke.
A team at the University of Cambridge are developing a machine learning tool that helps predict people’s risk based on their health records, thanks to joint funding from the British Heart Foundation and the Alan Turning Institute.
Researchers plan to use the long-term health records of over two million people in the UK to develop the algorithm.
Currently clinicians and GPs use risk calculators as part of the ‘NHS Health Check’ to asses a patient’s 10-year risk of developing heart or circulatory problems.
But these calculators only take into account a patient’s health at the time it is used, rather than including their medical and family history.
They also don’t account for how a patient’s risk factors have changed over time or differentiate the risk by specific heart and circulatory diseases, such as heart attacks, strokes, heart failure or abnormal heart rhythms.
The algorithm will use a wealth of information on people’s long term health records; map past trends in each patient’s health; and separate and classify the risk for each type of disease.
Via Dominique Godefroy
Researchers have used artificial intelligence to support the instant diagnosis of one of the top causes of blindness, diabetes-related eye disease, in its earliest stages.
Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of vision loss in adults and its impact is growing worldwide, with 191 million people set to be affected by 2030.
There are no early-stage symptoms and the disease may already be advanced by the time people start losing their sight. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a dramatic difference to how much vision a patient retains.
Now a team of Australian-Brazilian researchers led by RMIT University have developed an image-processing algorithm that can automatically detect one of the key signs of the disease, fluid on the retina, with an accuracy rate of 98%.
Lead investigator Professor Dinesh Kant Kumar, RMIT, said the method was instantaneous and cost-effective.
"We know that only half of those with diabetes have regular eye exams and one-third have never been checked," Kumar said.
"But the gold standard methods of diagnosing diabetic retinopathy are invasive or expensive, and often unavailable in remote or developing parts of the world.
"Our AI-driven approach delivers results that are just as accurate as clinical scans but relies on retinal images that can be generated with ordinary optometry equipment.
Via Dominique Godefroy
Radiology can once again situate itself at the center of patient care by embracing emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), RSNA 2018 President Dr. Vijay Rao said in her opening address. Radiologists must do their part to make this future a reality.
"We will need to embrace AI rather than fear it," Rao said. "We will need to recommit to the patient-centered model of radiology ... develop the necessary ethical and medical-legal procedures for protecting data as well as machine-learning algorithms ... [and] form cross-sector partnerships with our colleagues in other specialties."
Such efforts should be geared toward building a transformational framework for the profession -- one that will allow the next generation of radiologists to thrive, she noted. This will help shape the future of radiology into one in which "radiologists have been empowered by technology, not replaced by it."
"It is a future in which radiologists' capacity to provide improved patient care has been dramatically increased," she said. "And finally, it is a future in which we have achieved our long-standing goal of practicing at the epicenter of care, providing value to both the patient and our physician colleagues."
Transforming radiology
The rise of digital imaging, along with the lack of interoperability of systems, the shortage of radiologists, and physician burnout, in recent years has contributed to an increase in demand for value-based imaging, according to Rao, who is the David C. Levin professor and chairwoman of radiology at Thomas Jefferson University and hospitals.
AI and machine learning have emerged as a means of meeting this demand -- potentially enabling radiologists and other clinicians to harness the large amount of complex imaging data available even more effectively, she noted. Yet the rapid growth of these technologies has also spurred a sense of concern and even fear in the medical community.
"However, I don't believe AI will ever replace radiologists," she said. "In fact, much the opposite: I believe more firmly than ever that AI has the potential to enhance the profession and transform the practice of radiology worldwide. It'll allow radiologists to spend more time on initiatives that will benefit both patients and physicians."
Via Dominique Godefroy
Healthcare organizations that want to get ahead in 2019 will need to prioritize the use of artificial intelligence, virtualized care, and technologies that offer intuitive user experiences, according to Forrester’s predictions for the upcoming year.
The ability to aggregate, analyze, and utilize big data to identify business opportunities and engage users will become even more valuable as traditional healthcare entities battle for market supremacy against a new wave of technology powerhouses, the survey-based brief says.
“Major disruptors, like Amazon and Walmart, will make good on their promises, delivering the personalized experiences that customers have been yearning for from healthcare organizations (HCOs),” the report projects, leaving providers and payers with a strong imperative to leverage the data they have to offer similar benefits to users.
“HCOs need to develop raving fans to survive, as all sectors face the entrance of new disruptors looking to own more of the customer journey,” Forrester added. “They must build digital experiences, including virtual care, based on an understanding of the customer’s evolving needs. Great customer experiences will be crucial to drive loyalty and revenue.”
Advanced analytics capabilities, including the use of tools driven by artificial intelligence, will be required to fulfill these expectations.
Healthcare organizations will need to let go of outdated measurement processes and approach the development of user-friendly systems in the same manner as other industries, the report stresses.
Star ratings and CAHPS scores may become less important as providers and health IT developers adopt new measurements for engagement and satisfaction.
Via Dominique Godefroy
There seem to be almost endless ways artificial intelligence (AI) could transform healthcare, such as preventing disease and improving diagnoses and treatment, but for pharma there is a very real, near-term issue to solve – the escalating price and dwindling returns on R&D.
The AI revolution is being driven by massive leaps forward in computing power and an increase in access to health-related data sets that have made AI a powerful mining tool, able to identify patterns and relationships between data points that might never be identified by human researchers.
For pharma, much of the near-term excitement about AI stems from its potential to improve drug discovery and development, not least because using the technology promises to liberate researchers from the constraints of ‘perceived wisdom’ based on prior experience and expectations, unlocking new treatment pathways.
According to a Deloitte report, AI ‘can help analyse large data sets from sources such as clinical trials, health records, genetic profiles and preclinical studies; within this data, it can recognise patterns and trends and develop hypotheses at a much faster rate than researchers alone.’
Deloitte also suggests AI can help improve study design and decision-making in clinical trials, improving recruitment and enrolment, adherence and real-time clinical trial monitoring, which are all expensive parts of the drug development process. And applying AI to real-world evidence – another hot topic in pharma – could help companies predict performance of certain trial sites, anticipate drop outs and even predict outcomes.
Via Dominique Godefroy
My stomach is killing me!”
“I’m sorry to hear that,” says a female voice. “Are you happy to answer a few questions?”
And so the consultation begins. Where’s the pain? How bad is it? Does it come and go? There’s some deliberation before you get an opinion. “This sounds like dyspepsia to me. Dyspepsia is doctor-speak for indigestion.”
Doctor-speak, maybe, but it’s not a doctor speaking. The female voice belongs to Babylon, part of a wave of new AI apps designed to relieve your doctor of needless paperwork and office visits—and reduce the time you have to wait for medical advice. If you’re feeling unwell, instead of calling a doctor, you use your phone to chat with an AI.
The idea is to make seeking advice about a medical condition as simple as Googling your symptoms, but with many more benefits. Unlike self-diagnosis online, these apps lead you through a clinical-grade triage process—they’ll tell you if your symptoms need urgent attention or if you can treat yourself with bed rest and ibuprofen instead. The tech is built on a grab bag of AI techniques: language processing to allow users to describe their symptoms in a casual way, expert systems to mine huge medical databases, machine learning to string together correlations between symptom and condition.
Babylon Health, a London-based digital-first health-care provider, has a mission statement it likes to share in a big, bold font: to put an accessible and affordable health service in the hands of every person on earth. The best way to do this, says the company’s founder, Ali Parsa, is to stop people from needing to see a doctor.
When in doubt, the apps will always recommend seeking a second, human opinion. But by placing themselves between us and medical professionals, they shift the front line of health care. When the Babylon Health app started giving advice on ways to self-treat, half the company’s patients stopped asking for an appointment, realizing they didn’t need one.
Babylon is not the only app of its kind—others include Ada, Your.MD, and Dr. AI. But Babylon is the front-runner because it’s been integrated with the UK’s National Health Service (NHS), showing how such tech could change the way health services are run and paid for. Last year Babylon started a trial with a hospital trust in London in which calls to the NHS’s non-emergency 111 advice line are handled partly by Babylon’s AI. Callers are asked if they want to wait for a human to pick up or download the Babylon-powered “NHS Online: 111” app instead.
Via Dominique Godefroy
Researchers used people's Facebook data and their medical records to detect early symptoms of a mental health problem. In research described the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, scientists analyzed language from study participants' Facebook status updates to predict future diagnoses of depression. The researchers say their technique could lead to a screening tool that identifies people in need of mental health support and formal diagnosis, while raising serious questions about health privacy. If this line of inquiry sounds familiar, you're not imagining things: Scientists have been studying the association between Facebook and the mental state of its users for years—often without the consent of the people being examined study subjects. Earlier this decade, scientists at Facebook and Cornell conducted an infamous emotional contagion study, which targeted the moods and relationships of more than half a million Facebook users without their knowledge. But many scientists continue to use above-board research methods to access Facebook's data. For instance: By asking study participants to provide their consent, log into their accounts, and share their data—all in person—to provide one-time access to said data. The overhead is tremendous; it can take years to amass a large enough sample population using in-person study recruitment. Yet the effort can be worth it to social science researchers, many of whom regard Facebook's trove of user information as the most significant data repository in the history of their field. read more at https://www.wired.com/story/your-facebook-posts-can-reveal-if-youre-depressed/ also check out the opinion piece referencing this post at http://wordpress.futurism.com/ai-depressed-facebook-posts/
Via nrip
Google's artificial intelligence team has developed an algorithm that's like "spell check" for pathologists, the doctors responsible for diagnosing cancer patients through images of their cells.
In two papers published Friday, Google found that its algorithm complemented what the pathologists were able to pick up from the images in terms of determining how much patients' cancers had spread in their lymph node tissue.
"This represents a demonstration that people can work really well with AI algorithms than either one alone," Yun Liu, a member of the Google AI team and an author on the papers, told Business Insider.
Via Dominique Godefroy
Chinese tech giant Tencent and London medical firm Medopad have teamed up to use artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease.
A camera captures the way patients move their hands to determine the severity of their symptoms.
The research team has trained the system with existing videos of patients who have been assessed by doctors, working with King's College Hospital in London.
"We use the AI to measure the deterioration of Parkinson's disease patients without the patient wearing any sensors or devices," explains Dr Wei Fan, head of the Tencent Medical AI lab.
The aim is to speed up a motor function assessment process, which usually takes more than half an hour.
Using smartphone technology developed by Medopad, the hope is that patients could be assessed within three minutes - and might not even have to attend a hospital.
Medopad is a London-based firm that has been developing apps and wearable devices to monitor patients with various medical conditions.
It has been growing fast - but is a minnow compared with Tencent, which is spearheading China's huge investment in AI.
Via Dominique Godefroy
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...













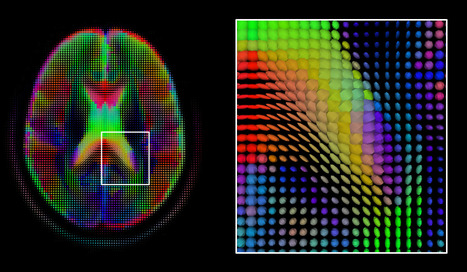
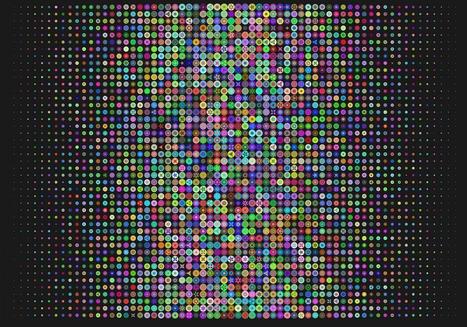














Comment fonctionne ChatGPT ?
Technologie : Cet article vous plonge dans les rouages de ChatGPT, le chatbot d'IA extrêmement populaire. Alors, si vous voulez savoir comment s'opère la magie de l'IA générative, lisez la suite.
Learn more / En savoir plus / Mehr erfahren:
https://www.scoop.it/topic/21st-century-innovative-technologies-and-developments/?&tag=ChatGPT
https://www.scoop.it/t/21st-century-innovative-technologies-and-developments/?&tag=AI
https://www.scoop.it/topic/21st-century-innovative-technologies-and-developments/?&tag=Ethics